
22-04-2024 | Noticias-en, Opinions
Law 27,739 sanctioned by the Congress of the Argentine Republic has come into force, which introduces important modifications in the current legislation on the prevention and repression of Money Laundering (ML), Financing of Terrorism (FT) and Financing of the Proliferation of Weapons. Mass Destruction (FP).
These reforms, motivated by Argentina’s Fourth Mutual Evaluation Round, are aligned with international standards established by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and are based on the risks identified in the corresponding national evaluations.
Some of the main points on which the modification deals are:
1.- Risk-Based Approach : The new legislation also establishes the application of a Risk-Based Approach for all regulations related to Regulated Entities. This means that preventive and control measures will be adapted according to the level of risk of each entity or activity, allowing greater effectiveness in preventing money laundering.
2.- Expansion of the list of Obligated Subjects . New actors have been included such as issuers, operators and collection and payment service providers, non-financial credit providers and virtual asset service providers. In addition, a section is added on non-profit organizations, which, although they are no longer obliged to the FIU, must undergo a risk analysis to avoid the financing of terrorism. This implies establishing proportional measures to mitigate the identified risks.
Also highlighted are the categories of lawyers, who will be obligated subjects when they operate on behalf and by order of a third party in: a- purchase and sale of real estate; b- administration of goods and assets; c- management of bank, savings and securities accounts, d- organization of contributions for legal entities; e- creation, management and commercial transactions of legal entities. Public accountants and public notaries remain on the list of previously established subjects.
3.- Registration of final beneficiaries . The reform creates the Public Registry of Final Beneficiaries under the jurisdiction of the AFIP. This centralized registry will collect complete and up-to-date information on the country’s beneficial owners, providing a crucial tool to combat financial opacity and improve transparency in economic activities. In addition, the regulations introduce key definitions, such as “final beneficiary,” and expand the criminal types related to money laundering, covering environmental crimes and financing of weapons of mass destruction. Different levels of access to information are also established for public and private entities, eliminating fiscal secrecy in relation to registry data. These measures, together with the inclusion of independent professionals in the obligation to report suspicious transactions, strengthen the legal framework and promote financial integrity in Argentina.
4.- Registry of Virtual Asset Service Providers : A registry of Virtual Asset Service Providers (PSAV) is created by the National Securities Commission (CNV), with clear definitions on virtual assets and suspicious operations.
5.- New Crimes : Argentina has integrated the crime of Financing the Proliferation of Weapons of Mass Destruction into its Penal Code. This measure is added to the regulations of the Financial Information Unit and obliges Obligated Subjects to include it in their prevention programs. In addition, the scope of article 306 has been expanded, including “property or other assets” in the crime of financing terrorism.
6.- Modification of the crime of money laundering . Article 303 of the Penal Code has undergone significant changes, with the threshold of punishment being raised to 150 minimum vital and mobile salaries (no longer a fixed amount of $300,000), also incorporating the verb “acquire” as a typical action. In addition, the prison sentence in the attenuated criminal type has been replaced by a financial fine. On the other hand, article 41 quinquies has been modified to include terrorism crimes in accordance with international conventions ratified by the country. These modifications impact the measurement of punishment, integrating crimes such as financing the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction. Despite these changes, fortunately article 305 maintains its effectiveness, allowing the definitive confiscation of assets in cases of money laundering, even in situations of extinction due to prescription.
7.- Updated Sanctions : The list of sanctions to be applied by the FIU to Obligated Subjects in case of regulatory non-compliance is updated, along with adjustments to the level of penalties. The legislation now reflects recent provisions of the FIU, allowing corrective actions prior to the opening of administrative proceedings for detected irregularities. In addition, the amounts of possible fines have been increased and the option of disqualifying the Compliance Officer as a sanction has been introduced.
8.- Expansion of Powers of the FIU : Its powers are expanded to strengthen the fight against ML/TF. Now, the subjects reached will not be able to oppose banking or professional secrecy in certain cases. A risk-based internal control system will be implemented and a registry of Independent External Reviewers will be established. In addition, key information will be provided through guides and seminars to improve the detection and reporting of suspicious operations. The supervision procedures may conclude in corrective actions or administrative summaries depending on the severity of the deficiencies detected.
9.- Parliamentary Control: A new control is implemented through the Bicameral Commission for Oversight and Intelligence Activities Agencies, establishing the obligation for the FIU to appear before this commission, providing reports, opinions and advice as required.

By Diego García Austt, lawyer specializing in Economic Crimes | Compliance Latam collaborator.

18-04-2024 | Noticias-en, Opinions
In Peru’s vibrant tourism scene, where cultural and natural wealth attracts visitors from all over the world, the hotel industry plays a crucial role. However, behind the warmth and hospitality it offers its guests, there is a vital but often underestimated aspect: compliance, understood as the culture of integrity that must govern organizations.
Compliance in the tourism sector is not only a matter of following rules and regulations imposed by the authorities, but, as we said, it is part of an organizational culture that allows building and maintaining customer trust, safeguarding the reputation of companies and, ultimately, foster an environment of fair and sustainable competition.
One of the main challenges facing the Peruvian hotel industry in terms of compliance is the need to quickly adapt to a constantly changing regulatory environment. From tax regulations to health and safety requirements, tourism-related businesses must be aware of a wide range of regulations to operate effectively and ethically.
One of these challenges is presented in its consideration as a subject obliged to have a money laundering and terrorist financing prevention system (splaft), a system that is supervised by the Financial Intelligence Unit (UIF) [ 1] .
To face this scenario, transparency and integrity are essential. Robust compliance programs must be established that address areas such as the prevention of corruption, money laundering and respect for labor rights. Additionally, ongoing staff training is essential to ensure that all employees understand and comply with established policies and procedures.
Importantly, regulatory compliance goes beyond simply following the laws. It is about promoting an organizational culture rooted in ethical principles and solid values. This involves promoting corporate responsibility and commitment to environmental and social sustainability. Companies that take a comprehensive approach to compliance not only minimize the risk of legal sanctions, but also create a competitive differentiator that resonates with increasingly aware consumers.
However, implementing and maintaining a strong compliance program is no easy task. It requires investment of time, resources and, most importantly, genuine commitment from senior management. It is essential that industry leaders recognize the strategic importance of compliance and integrate it into corporate decision making.
Additionally, given the impact of technology on the hospitality industry, companies must be attentive to the cybersecurity and data protection implications. The collection and storage of personal guest information carries great responsibility, and it is crucial that appropriate measures are implemented to protect data privacy and security.
In view of the importance of compliance in the Peruvian tourism industry, it is essential that business leaders understand its strategic value and the need to implement it in their organizations. Only through active commitment to ethical principles and legal standards will tourism companies be able to strengthen their reputation, earn the trust of their clients and remain competitive in an increasingly demanding market.
Therefore, we invite all managers in the hospitality sector to seriously consider implementing compliance in their companies as a long-term investment in the integrity and sustainability of their businesses. Adopting a culture of ethical compliance will benefit not only the company’s internal relations but also its corporate image, contributing to strengthening the growth of the tourism sector in Peru.
[1] Institution dependent on the Super Intendency of Banking and Insurance (SBS).
For more information contact:

Mario Pinatte | CPB Partner | mpinatte@cpb-abogados.com.pe

01-04-2024 | Noticias-en, Opinions
As women in the Compliance field, we understand that gender equality is, in addition to an essential right, the fundamental basis for building a prosperous and equitable world. This approach is closely aligned with Sustainable Development Goal No. 5 (“SDG 5”) of the United Nations Global Compact, which seeks to promote gender equality and the empowerment of all women and girls in all aspects of life. .
Despite the progress made in recent decades, women and girls around the world still face significant barriers to enjoying this equality, especially in key areas such as education, healthcare, employment and participation in decision-making. political and economic decisions. The reality that comes from being exposed reflects a challenge that requires continuous commitment from all sectors of society.
In the corporate context, companies have a crucial role to play in promoting gender equality. It is not only about adopting internal policies and procedures to guarantee equal rights and employment opportunities, but also about investing in economic empowerment programs that benefit women and girls in the communities where they operate, aiming to build more inclusive work environments, fair and productive.
In accordance with SDG 5, some of the practices that companies can implement include, but are not limited to:
- Create an Equality Plan with specific commitments, measures and objectives to promote and achieve gender equality within the organization.
- Monitor and ensure that all company policies include a gender perspective and that the business culture promotes equality and integration.
- Implement procedures aimed at promoting an increase in the number of women at all levels and positions within the organization, especially in positions of responsibility and management.
- Develop a training plan on gender, which includes topics such as human rights and non-discrimination, for all departments and areas of the organization.
These actions not only meet the objectives of SDG 5, but also contribute to building a more equitable and sustainable environment for present and future generations. Additionally, they foster a more productive and enriching work environment for all employees, regardless of gender.Principle of the form.

By Lucía Rodríguez Wikman, Lawyer | CIEMSA

25-03-2024 | Noticias-en, Opinions
Introduction
The choice of the title is not arbitrary and advances our opinion that giving space in these areas and, in all, to women is not an exercise for diversity, because, among other reasons, not even numerically, women are a minority. If this is not the case, it does not seem reasonable that, in specific areas, gender should be treated this way.
We chose this topic because we frequently see spaces for discussion about the inclusion of women in the Latin American labor market. However, there are fewer spaces that deal with the inclusion of women in the administration and representation bodies of public or private legal entities.
Data
The World Economic Forum report, in reference to the “Global Gender Gap” of June 2023, indicated that, in general terms, it will take 53 years to close the gender gap in Latin America and the Caribbean.
In particular, the push to increase the role of women on boards may be even slower, compared to that in other areas of activity. In a work by the OECD2 “OECD Corporate Governance Factbook 2023” the following data is indicated in relation to the participation of women on the boards of directors of listed companies in the following Latin American countries:
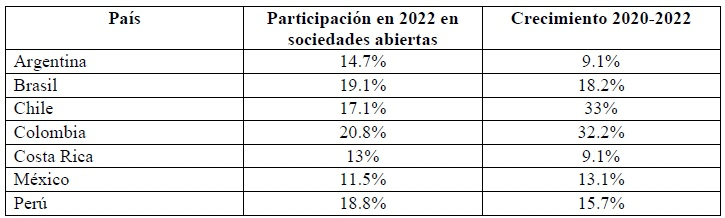
As can be seen, inclusion in these forums is low. The acceleration of the inclusion of women in these areas has been handled in different ways depending on the country. Some propose state intervention through regulations (for example, with the establishment of mandatory quotas). Other countries have opted to disclose the gender composition of board members; while another group has established less rigorous mechanisms, such as the setting of voluntary objectives or goals or simply a collaborative approach.
To mention a case that is familiar to us, in India, according to the Companies Act, 2013 as amended, the participation of at least one woman on the boards of directors of companies is required.
According to a Harvard Business Review article “What Happened When India Mandated Gender Diversity on Boards”3, this movement began in 2003 in Norway, which established that boards should have 40% women in their composition. However, as also noted in the aforementioned work, it has been suggested that the response to these initiatives may result in the election of women to join the boards of directors with the sole purpose of complying with the law with the quota requirements without their presence can be considered legitimate. Likewise, one of the effects of the original Norwegian quota is that a small group of prominent women were appointed as directors in multiple companies.
According to the same work, this effect did not occur in India, where the law managed to significantly expand the group of different women who served as directors.
Some reflections
We asked ourselves, then, whether the issuance of standards would be the most effective way to increase the real participation of women on company boards.
It seems clear that a regulation of this nature requires, among other measures, prior attention to the issue of women’s participation in leadership positions, to avoid the repetition of phenomena such as the reports of concentration of appointments in few women or of lack of legitimacy. It is necessary, then, to educate and encourage the occupation of these spaces and not only impose participation.
And in all this, companies have a main role in adjusting their organizational culture and business administrative perspective. A company with a perspective of integration, diversity and gender focus should be a pioneer in these issues, enhance and promote it from its basic core, without waiting for the existence of an obligation. And this reflection is even more applicable to business conglomerates that are established. in different jurisdictions since it would not make sense to adopt a gender quota according to legislation if active and global policies for the participation of women in all positions and also on boards of directors are not maintained. This will imply a change and will generate resistance, but it cannot be postponed.
By Ana Cristina Peña, Crime Prevention Officer Latin America at Tata Consultancy Services.
—————————————————————-
1 World Economic Forum “Global Gender Gap 2023” retrieved from https://www.weforum.org/publications/global-gender-gap-report-2023/ consulted on March 18, 2024.
2 OECD (2023), OECD Corporate Governance Factbook 2023, OECD Publishing, Paris, https://doi.org/10.1787/6d912314-en consulted on March 18, 11, 2024.
3 HBR “What Happened When India Mandated Gender Diversity on Boards”, February 2021 retrieved from What Happened When India Mandated Gender Diversity on Boards (hbr.org)

19-03-2024 | Noticias-en, Opinions
In the field of corporate compliance, the effective implementation and implementation of programs and systems for the prevention and management of risks such as money laundering and corruption is increasingly important. One of the most recent documents from the United States Department of Justice (DOJ) points to this conclusion, which consists of a guide for the evaluation of corporate compliance programs, aimed at federal prosecutors in charge of prosecuting companies for participating in acts of corruption and transnational bribery, in application of the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA).
The aforementioned guide is intended to give prosecutors tools to “make informed decisions about whether, and to what extent, the company’s compliance program was effective at the time of the crime and is effective at the time of the accusation” in order to determine its merit to exonerate liability or mitigate the penalty imposed on the company. The second of the three cardinal aspects that the guide gives to evaluate the programs, inquires about whether the company’s compliance program has adequate resources and powers to function effectively, and the third of the criteria to answer this question is directly related with compensation and consequence management structures, in other words, establishing incentives for compliance and disincentives for non-compliance.
The Superintendency of Companies of Colombia, as regulator of the most extensive compliance programs in the country (SAGRILAFT and PTEE), shares the opinion that sanctions and compensation schemes are an important, even essential, element of an effective compliance program. Therefore, both Circular 016 of 2020 (SAGRILAFT) and Circular 011 of 2021 (PTEE) instruct obligated subjects to include this element in their programs, as follows:
– Section 5.1.2. of Circular 016 of 2020 says that: “The SAGRILAFT must include sanctions or consequences for employees, administrators, associates or third parties, for non-compliance or non-observance of its provisions.”
– Section 5.1.5.3.2, literal g, establishes that the compliance officer must implement “internal investigation procedures in the Obligated Entity to detect non-compliance with the PTEE and Acts of Corruption”; and section 5.1.2. It says that “the PTEE must include, in a clear and simple way, the consequences of violating it.”
Additionally, the Superintendency clarified, in Official Letter 220-091819 of July 11, 2021, that “the obligated subjects will determine the mechanisms that will allow them to evaluate, monitor and control the risks and, in turn, will establish the relevant sanctions for non-compliance with the system in accordance with its organizational structure, sanctions that must cover both employees, administrators, associates or third parties. (…) Therefore, it is up to each obligated company to determine, in each particular case and in accordance with the characteristics of its organization, the sanctions applicable to associates who fail to comply with SAGRILAFT.”
Colombian companies that have been implementing these programs since 2016 have focused on following the regulations’ instructions to the letter, including simple sanctioning regimes in their compliance systems. In practice, the most common scheme consists of classifying non-compliance with the duties and obligations derived from compliance policies and procedures as disciplinary offenses, and the compliance area, in these cases, usually plays the role of investigator who presents the case. before the disciplinary authority. The consequences for non-compliance have then been limited, with good judgment, to what is permitted by labor regulations, from reprimands to suspensions from their duties without remuneration, and in serious cases even the termination of the employment contract with just cause, after developing a disciplinary due process. It is worth remembering that, according to the substantive labor code, disciplinary sanctions with pecuniary consequences are completely prohibited, except in cases in which the worker has unjustified delays or absences, in which case the hours or days not worked can be deducted from the salary. Such regulation completely prevents the imposition of economic sanctions for lack of compliance.
On the other hand, incentive or compensation schemes to encourage compliance seem to still be a field insufficiently explored by companies, which is a real shame because, although there are currently insufficient parameters to measure the effectiveness of adopting compensation schemes in compliance programs, the truth is that in other areas of the development of corporate culture, incentives have proven to be useful tools to promote cultural changes and the internalization of corporate values, so, from the perspective of corporate compliance, it would be a practical recommended to help translate paper compliance programs into the reality of companies.
Contrary to the situation in the United States, Colombian regulations do not require or suggest specific models of incentives and sanctions as a mandatory requirement in compliance programs. The assessment of these programs within the framework of the administrative sanctioning procedure lacks detailed government guidelines, and there is nothing to indicate that the compensation and sanction schemes are rigorously evaluated as a component of effectiveness to mitigate the administrative responsibility of legal entities in the framework of the sanctioning procedures initiated under the Anti-Corruption Statute (Law 1474 of 2011) and the Transnational Bribery Law (Law 1778 of 2016). However, Colombian regulation tends to imitate North American trends, which have become a true compliance standard for Latin America, therefore, it makes sense that we begin to take the tools seriously to make our compliance programs true instruments. for the prevention and management of risks in companies.
BONUS: Some ideas on incentive and sanction schemes to reinforce the compliance culture in your company:
Incentives:
• Public recognition: Reward ethical and transparent employees in meetings or internal communications.
• Ethical bonus program: Offer financial bonuses to employees who demonstrate outstanding ethical behavior.
• Ongoing training: Provide ethics and compliance training opportunities, with incentives for completing courses and certifications.
• Extra days off: Provide extra days off as a reward for maintaining high ethical and compliance standards.
• Participation in decision-making: Invite ethical employees to participate in key decision-making processes to foster their commitment.
Sanctions:
• Temporary suspension: Impose temporary suspensions on those who violate ethics or compliance policies.
• Affected performance review: Link performance evaluation to ethical conduct, so that those who do not comply face consequences in their reviews.
• Phased removal process: Implement a system of progressive warnings before termination for cases of unacceptable ethical conduct.
• Prohibition of promotions: Prevent promotions and promotions for those who have violated ethical policies until they demonstrate a change in their behavior.
It is important to adapt these measures according to the culture and specific needs of the company, promoting a balanced approach between incentives and sanctions to achieve effective results.

By Nicolás Castro Márquez, corporate criminal lawyer, Posse Herrera Ruiz.

13-03-2024 | Noticias-en, Opinions
Last January, Fundación Generación Empresarial presented the results of a study that has been carried out annually for 18 years. A total of 165 public and private institutions, for-profit and non-profit, large and small, were encouraged to be part of the Recognition of Commitment to Integrity, a process that allows them to know how they live the values, and which culminated with a ceremony that He distinguished those that stood out the most. This is the largest number that has participated in this activity that includes the application of the Barometer of Values and Organizational Integrity and the delivery of documentation that certifies good practices. More than 45 thousand people from all walks of life responded to this survey about the advancement of the “culture of integrity” in their workplace, communicating with actions and not words, that integrity is a central value in their work, and that they are making genuine efforts to improve themselves.
On average, people who responded to the Barometer expressed themselves positively about the place where they work. They said that there are established values and they are promoted (87%), that they are actively disseminated (82%) and that managers act in accordance with them by setting an example (72%). They also expressed concern that their organization could become involved in corruption scandals (one in three people). These figures are reason to be optimistic. But the situation in the country makes us be cautious because, in the circumstances we live in today, it is not integrity that monopolizes the headlines, but corruption.
The Barometer measures perceptions and the Accreditation Guidelines record the institutionalization of practices of the Ethics and Compliance Program. Today we talk about “compliance” to refer to the legal requirements that must be met, but if this becomes an issue that is entrusted only to lawyers, it does not help much. This way, behaviors are not changed much.
The focus should be on corporate governance and culture, that is, the way things are expected to be done, how the organization is run and decisions are made at the top level. This implies that “the tone at the top”, which refers to the actions promoted by managers, must be effective in strongly communicating the ethical implications of behavior at all levels of the organization. Your message should be that you have to strive to “do things right,” and that you trust people’s ability to self-regulate their behavior. The best way to make this message credible is through ethical leadership that “speaks from action” and “zero tolerance” for abuse and corruption.
Not only people with values-based behavior win. Whoever acts accordingly, whatever their role, will feel the satisfaction of having done their best and this will have a positive impact on the work environment. The same goes for organizations. Their effort to get things done supports the integrity of the entire country. Hence the importance of all organizations “dare to be better.” Measuring yourself is the first step of change, as it shows the intention to renew yourself. But we must move beyond measurement… it is time to act.

By Fernanda Hurtado, General Manager FGE and Compliance Latam Collaborator.








